Overview
This page will explain the overview of the crazyflie ROS 2 nodes:
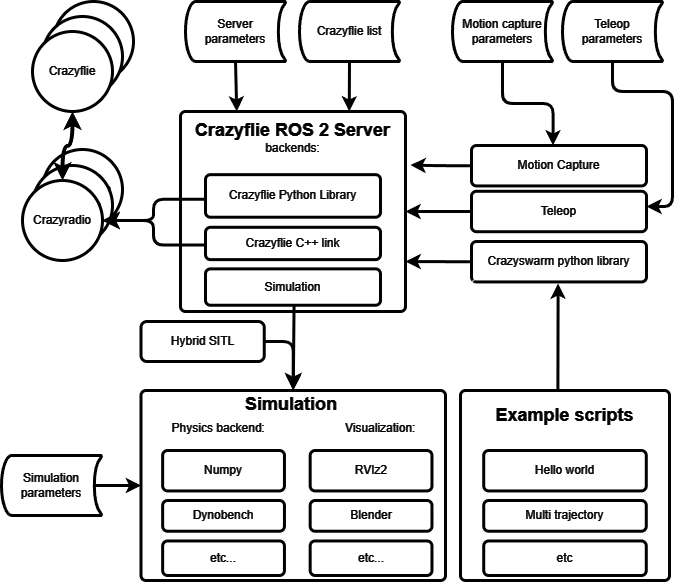
Explanation per package
In the source code of the Crazyswarm2 (Crazyflie ROS 2) project, there are several packages that we will explain here:
crazyflie/: The package that contains the crazyflie server nodes and the crazyflies.yaml.
crazyflie_py/: The package that contains the python library that wraps around the ROS 2 services and topics that connects with the crazyflie server nodes.
crazyflie_examples/: The package that contains examples of using the crazyflie ROS 2 package. See ROS 2 Tutorials.
crazyflie_interfaces/: The package that contains all msgs and srvs for the crazyflie ROS 2 project.
crazyflie_sim/: The package that contains our simulator.
Crazyflie server
The crazyflie server node connects multiple Crazyflies with on or more Crazyradio PA dongles.
It has three backends that you can choose from:
cpp: This is based on the crazyflie-link-cpp on the lowest layer.
cflib: This is based on the crazyflie-lib-python up until the logging, parameter, and command sending handling.
sim: Our simulator behaves like a regular backend, offering ROS 2 topics and services, see below for more details on the simulation.
It handles several low level communication aspects with the Crazyflies:
Parameter to ROS 2 parameters handling: It receives the parameter ToC from the Crazyflie, transforms it into ROS 2 parameters, and sets the CF2 parameters based on the crazyflies.yaml input.
Logging to ROS 2 topics handling: The server sets up logblocks for data streaming in the crazyflie, and transforms the received variables into ROS 2 topics.
Run-time configuration: Both parameters and logging can be configured in run-time while the server is connected with the Crazyflies. Please check Usage.
It also setups several flight command services:
Takeoff / Land / GoTo: With a single service command and a given height or coordinate, you can make the connected crazyflies take off, go to a position and land.
Upload / Start trajectory: You can upload a predefined trajectory and indicate if the Crazyflies need to start flying it.
Emergency : To turn off the motors in case something goes wrong.
/all or /cf2 : The services are setup either for all crazyflies to respond to, or each individual crazyflie, depended on the prefix.
Simulation
The simulator uses the Crazyflie firmware as a software-in-the-loop (SIL). It provides the same ROS interface as the server and therefore can be used with C++ or Python user code.
Currently, the desired setpoint is visualized in rviz (see Usage) or a simple physics-based simulator can be used.
Support functionality with backends
Functionality |
Cpp |
CFlib |
Sim |
|---|---|---|---|
Parameters |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Logging |
|||
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
No |
Yes |
No |
Broadcasts |
Yes |
No |
n/a |
Manual control |
|||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
High-level control |
|||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Positioning System |
|||
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Misc |
|||
|
Yes |
Yes |
n/a |